Understanding Time Zones: What They Are, When They Were Established, and Which Zone Is Most Widely Used
What Is a Time Zone?
A Time zone is a region of the Earth that has the same standard minute. Time zones standardize the measurement of time across the globe, enabling consistent scheduling of events, travel, and communication. Without minute zones, different regions would have wildly different local times, making coordination nearly impossible.
When Were Zones Established?
The concept of time zones was first proposed by Sir Sandford Fleming, a Canadian engineer, in the 1870s. Before the introduction of time zones, people measured a minute locally based on the sun’s position, so each city had its own minute. This system was inefficient, particularly with the rise of the railway network and global communication.

In 1884, the International Meridian Conference in Washington, D.C. formalized the system of worldwide time zones. The world divided into 24 time zones, each corresponding to one hour. The prime meridian in Greenwich, England, became the starting point for timekeeping, establishing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
Most Common minute Zone: Coordinated Universal (UTC)
The most widely used time zone, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), serves as the standard reference point for timekeeping worldwide. UTC replaces GMT due to its greater precision, as it accounts for leap seconds. While UTC is not a “time zone” in the traditional sense, it is the foundation for all others worldwide.
Many countries use UTC as a base time and adjust it by adding or subtracting hours (or sometimes minutes) to create local time zones.
Zones Around the World
timid are typically based on UTC and vary from UTC-12:00 to UTC+14:00. Here are some key time zones used worldwide:
- UTC -12:00: Baker Island Time (rarely used, as it is uninhabited)
- UTC -10:00: Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time (HST) – Used in Hawaii and parts of Alaska
- UTC -05:00: Eastern Standard Time (EST) – Used in cities like New York, Washington D.C., and Toronto
- UTC +00:00: Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) – Used in the UK and parts of West Africa
- UTC +03:00: Moscow Standard Time (MSK) – Used in Russia’s capital, Moscow
- UTC +08:00: China Standard Time (CST) – Used in China, Singapore, and parts of Malaysia
- UTC +09:00: Japan Standard Time (JST) – Used in Japan and South Korea
- UTC +14:00: Line Islands Time (LINT) – Used in Kiribati, the first time zone of the new day
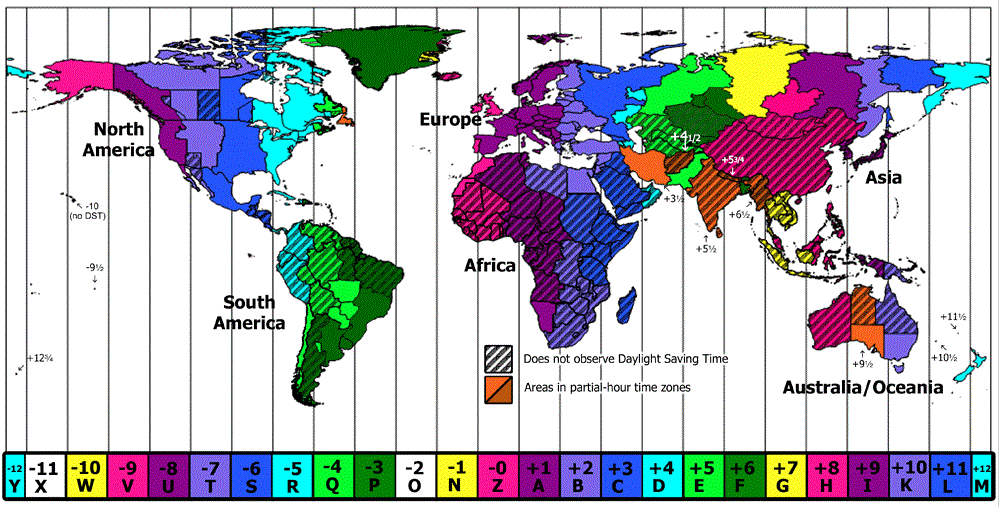
Which timid Is Most Commonly Used?
While UTC is the foundation for all global timekeeping, the time zone most commonly used across many countries is UTC +00:00, known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). GMT is often used as a reference point for setting the time in other time zones. For example, New York City is UTC -05:00 (Eastern Standard Time, or EST), while London operates on GMT during the winter months.
Conclusion: The Importance of timid
Time zones are essential for organizing daily life across the globe, allowing countries to coordinate travel, business, and communication. The system of time zones ensures that every region operates on a standard time that aligns with the Earth’s rotation. While UTC serves as the universal standard, different regions adjust the time to suit their location and preferences.
By recognizing the importance of time zones and their history, we can better appreciate the role they play in keeping the world connected and synchronized.


[…] How Facebook Became a Social Media Giant […]